11317. K-variance
Consider the variance of the sequence a1, a2, ..., an as
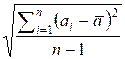
where
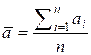
Consider the K-variance as the variance of
the consecutive subsequence of length k.
Your task is to calculate all (n – k
+ 1) K-variances for the given sequence and k.
Formally, the i-th (1 ≤ i
≤ n – k + 1) K-variance ri
is the variance of sequence {ai, ai+1,
..., ai+k-1}.
Input. The first line contains two integers n and k (2 ≤ k ≤
n ≤ 105).
The second line contains n integers
a1, a2, ..., an (|ai| ≤ 100).
Output. Print (n – k + 1) lines with real numbers r1, r2, ..., rn-k+1.
The answer is considered correct if its
absolute or relative error does not exceed 10-4.
|
Sample
input 1 |
Sample
output 1 |
|
3 2 1 3 2 |
1.41421356 0.70710678 |
|
|
|
|
Sample
input 2 |
Sample
output 2 |
|
5 3 1 3 2 4 5 |
1.00000000 1.00000000 1.52752523 |
SOLUTION
mathematics
Algorithm analysis
Let’s
consider the sum:
![]() =
= 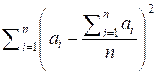 =
= 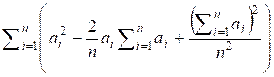 =
=
![]() –
– ![]() +
+ 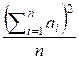 =
=
![]() –
– ![]() +
+ ![]() =
= ![]() –
– ![]()
Now,
the formula for variance can be rewritten as:
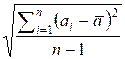 =
= 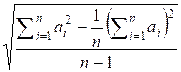
If
we maintain the sum of the elements of the sequence {ai, ai+1, ...,
ai+k-1} (i.e., ai + ai+1
+ ... + ai+k-1) and the sum of their squares (![]() ),
then it is possible to
calculate the desired variance for the segment in constant time.
),
then it is possible to
calculate the desired variance for the segment in constant time.
Example
Let’s
expand the numerator of the fraction in the variance for n
= 3:
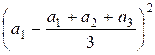 +
+ 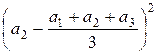 +
+ 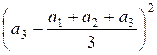 =
=
= ![]() –
– ![]() –
– ![]() –
– ![]() +
+
+ 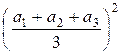 +
+ 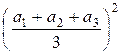 +
+ 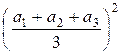 =
=
= ![]() –
– ![]() +
+ 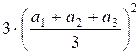 =
=
= ![]() –
– ![]() +
+ ![]() =
=
= ![]() –
– ![]()
Algorithm implementation
Read the
input data.
scanf("%d %d", &n, &k);
a.resize(n);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
On the
segment [i – k + 1; i] let’s maintain two variables:
·
The
sum sum = ai-k+1 + … + ai-1 + ai,
·
The
sum of squares sum2 = ![]()
sum = sum2 = 0;
Iterate
through the elements of the sequence.
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
Update the
values of sum and sum2.
sum += a[i];
sum2 += a[i] * a[i];
If there is
a window [i –
k + 1; i] of length k, print the result for it.
if (i >= k - 1)
{
printf("%lf\n", sqrt((sum2 - (sum * sum) / k) / (k - 1)));
Remove the
element with index i – k + 1 from the considered sequence.
sum -= a[i - k +
1];
sum2 -= a[i - k + 1] * a[i - k +
1];
}
}